What is a coating machine? Coating machines are essential in the pharmaceutical industry, where they play a pivotal role in producing high-quality tablets and capsules. These machines apply a thin, uniform layer of coating material to solid dosage forms like tablets, enhancing their stability, appearance, and functionality.
This article will explore how coating machines work, their components, and the critical steps involved in the coating process.

Boost Your Production Efficiency with Canaan’s Premium Coating Machines!
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, coatings serve several purposes.

First and foremost, they protect the active ingredients in a drug from environmental factors such as moisture, light, and oxygen, ensuring that the drug remains effective throughout its shelf life. Coating also improves the aesthetic appeal of a tablet, making it easier for patients to swallow and more pleasant in terms of taste and odor.
In addition to protection, coatings control the release of a drug. For example, sustained-release or delayed-release formulations are made possible by coating technology, allowing for more controlled and consistent therapeutic effects.
By selecting the right coating equipment, pharmaceutical companies can ensure their products meet high standards of quality, safety, and efficacy.
Coating machines are complex systems with several integral components, each contributing to the precision and effectiveness of the coating process. Here are the primary components involved:
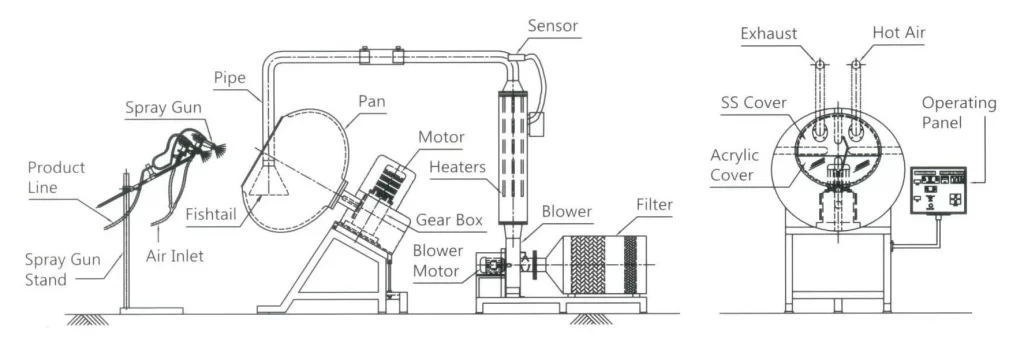
These components work in harmony to achieve a uniform coating that meets pharmaceutical standards.

The primary principle behind a coating machine is the continuous movement of tablets while they are sprayed with a fine mist of coating solution. This ensures even distribution of the coating across each tablet, with heated air blowing to dry the coating. The coating process typically involves applying multiple layers to achieve the desired thickness and effect.
Coating solutions can vary, from film coatings to sugar coatings, depending on the application. Film coatings are typically thinner and used to protect the tablet from the environment, whereas sugar coatings are thicker and more suited to masking unpleasant tastes.
| Step | Description |
| Preparation | Measure and prepare the tablets and coating solution (water-based or solvent-based). |
| Loading | Load tablets into the rotating coating pan to ensure even exposure to the spray system. |
| Warming | Preheat the tablets to remove moisture and help the coating stick better. |
| Spraying | Spray the coating solution evenly on the tumbling tablets using calibrated nozzles. |
| Drying | Use heated air to dry the coating, ensuring each layer solidifies without defects. |
| Repeating Process | Repeat spraying and drying until the required number of coating layers is achieved. |
| Cooling | Cool the tablets to harden the final coating and prevent sticking. |
| Discharging | Carefully remove the coated tablets for inspection or packaging to avoid damaging the coating. |
Coating machines are essential tools in pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring that every tablet or capsule meets rigorous quality standards. Whether you’re working with immediate-release or sustained-release formulations, having the right coating equipment can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of your production process.
Ready to enhance your coating process? Contact us to explore our range of coating machines designed to meet the highest industry standards.




Before any drug reaches a patient, it starts in a lab. That’s where formulas are tested, batches are checked, and quality is either confirmed or questioned. To do that work right, labs depend on the right equipment—tools that don’t just get the job done, but do it with precision. If you’re responsible for running or […]

Blister packaging is everywhere in pharma—from tablets to capsules to sample packs. It protects the product, extends shelf life, and improves patient safety. But for manufacturers, it’s more than just packaging—it’s a system built around speed, precision, and compliance. If you’re in pharma manufacturing or packaging procurement, here’s what you need to know about blister […]

If you’re deciding how to deliver a pharmaceutical or supplement product, the format you choose—liquid gels or tablets—will shape more than just how it looks. It affects how the product is made, how fast it’s absorbed, what kind of equipment you’ll need, and how the end user experiences it. Some actives work better in a […]